Abstract
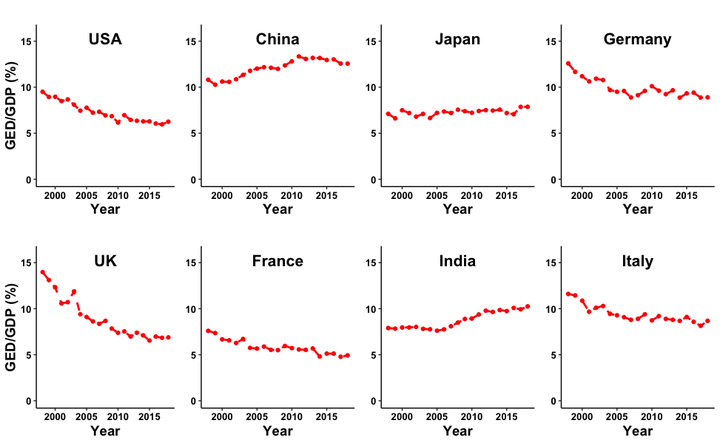
A persistent issue in environmental economics is whether growth is sustainable. Pollution is a key driver of sustainability, which we define as an economy exhibiting falling pollution damages at its balanced growth path. We deduct air pollution and carbon dioxide damages from the national accounts for 163 countries between 1998 and 2018. Global pollution intensity fell from 1998 to 2008, remaining flat thereafter. China highlights the importance of defining sustainability in terms of damages; between 2011 and 2018, physical measures of environmental quality improved, but monetary damage increased by 50 percent. Sustainability based on emissions ignores this rise in damage.
Type
Publication
National Bureau of Economic Research Working Paper Series